Understanding Structural Steel Construction
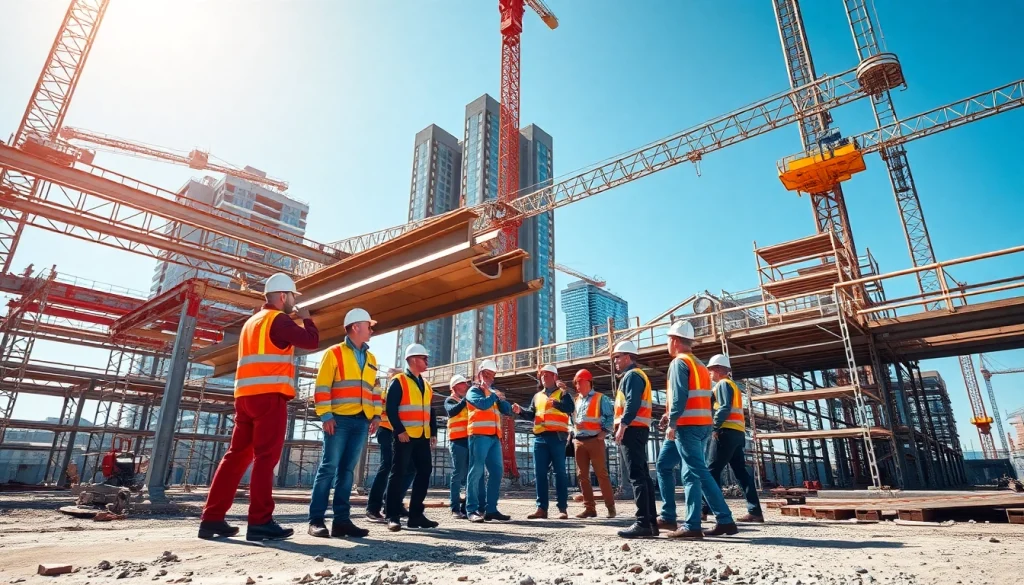
Structural steel construction is a transformative approach within modern engineering, providing robust solutions for building various infrastructures, from skyscrapers to bridges. This type of construction uses steel as the primary component, leveraging its high strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of structural steel construction, examining its definition, applications, advantages, and the essential planning and design considerations that underpin successful projects.
What is Structural Steel?
Structural steel is a category of steel used for making construction materials in a variety of shapes. These shapes are formed through a process of heating, cooling, and shaping, resulting in components such as beams, columns, and girders. Structural steel is designed to bear loads and provide support in buildings and bridges, making it an integral material in construction. Its specifications are standardized according to the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
Applications of Structural Steel in Construction
The applications of structural steel are vast and diverse, extending across multiple sectors. Some key applications include:
- Commercial Buildings: Skyscrapers and office complexes heavily rely on structural steel for their frameworks to support significant loads.
- Industrial Structures: Factories and warehouses use steel for durability against heavy machinery and storage needs.
- Bridges: Many bridges utilize structural steel to ensure longevity and strength, able to withstand traffic loads over time.
- Residential Buildings: Increasingly, homes are being built using structural steel for its modern aesthetic and resilience.
Advantages of Using Structural Steel
The advantages of incorporating structural steel into construction projects are numerous:
- Strength: Structural steel has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which means it can support heavy loads.
- Versatility: It can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of architectural designs.
- Speed of Construction: Pre-fabricated sections can be quickly assembled on-site, reducing build time significantly.
- Durability: Steel is resistant to many environmental factors, including termites, mold, and rot.
- Recyclability: Structural steel is 100% recyclable, which contributes to sustainable building practices.
Planning and Design Considerations
The foundation of any successful structural steel construction project entails meticulous planning and sound design practices. Several vital factors contribute to this process.
Key Factors in Structural Steel Design
The design of structural steel components must account for several key factors to ensure safety and stability:
- Load Types: Understanding the different loads, including dead loads (permanent/static) and live loads (temporary/dynamic), is essential.
- Building Codes: Compliance with local and national building codes is mandatory to ensure safety protocols are met.
- Material Properties: Considerations such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility of the steel are critical for design calculations.
Load-Bearing Calculations and Safety Standards
Load-bearing calculations must be precise to prevent structural failures. Engineers use various methodologies, like finite element analysis, to ensure that designs meet safety standards. Adhering to safety practices outlined by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and following guidelines developed by the AISC can further ensure the integrity of a building’s structure.
Integrating Structural Steel into Architectural Plans
Successful integration of structural steel into architectural designs requires collaboration between architects and structural engineers. This partnership ensures that the aesthetics of a building do not compromise its structural integrity. The use of steel allows for open floor plans and large spans, enhancing the functional and visual elements of a design.
Material Selection and Quality Control
Choosing the right materials and implementing comprehensive quality control measures are vital for the success and safety of structural steel construction projects.
Choosing the Right Structural Steel Grades
Structural steel is categorized into various grades based on its composition and properties. Common structural steel grades include:
- A36: A versatile structural steel used in a wide range of applications.
- A992: Standard for structural steel shapes used in buildings, providing excellent strength properties.
- A572: Used in high-strength applications, offering better weldability and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the appropriate grade depends on factors like environmental exposure, the magnitude of loads, and specific building requirements.
Importance of Quality Inspections
Quality control during the fabrication and installation phases is paramount. This includes inspecting materials for defects and verifying that proper welding and assembly techniques are implemented. Regular inspections can mitigate risks and ensure that the construction can withstand specified load requirements.
Addressing Common Material Deficiencies
Material deficiencies can lead to structural failures. Common issues include:
- Corrosion: Use of protective coatings and proper drainage can prevent rust formation.
- Weld Defects: Rigorous welding inspections can identify problems early on, allowing for correction.
Implementing a proactive quality assurance program can enhance the overall durability of the construction.
Construction Techniques and Best Practices
Successful implementation of construction techniques enhances not only safety but also project efficiency. Adopting best practices is influential in achieving project success.
Efficient Assembly Methods for Structural Steel
Construction techniques for structural steel assembly include:
- Pre-fabrication: Components are manufactured off-site, reducing on-site assembly time.
- Modular Construction: Structures are built in modules that are transported and installed quickly.
Both techniques optimize labor efficiency and reduce construction timelines.
Safety Protocols During Construction
Safety during construction should never be compromised. Some important safety protocols include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensuring all workers wear appropriate gear at all times.
- Site Safety Training: Regularly conducting training sessions to familiarize employees with potential hazards.
Implementing these precautions can significantly reduce workplace accidents.
Utilizing Technology in Steel Assembly
Technological advancements have revolutionized the structural steel construction industry. Using Building Information Modeling (BIM) improves accuracy in design, while robotics in manufacturing can expedite processes. Additionally, mobile technology can enhance communication among teams, ensuring that everyone is updated on project progress and any arising issues.
Project Management and Cost Efficiency
Effective project management is crucial for delivering structural steel projects on time and within budget. Key considerations include cost estimation, resource management, and project assessments.
Estimating Costs for Structural Steel Construction
Estimating costs involves analyzing several factors, including raw material prices, labor costs, and project timelines. A comprehensive understanding of these components aids in providing accurate predictions, which is key to budgeting effectively.
Managing Time and Resources Effectively
Project managers must prioritize time and resource management. Utilizing project management software can create timelines, set milestones, and assign tasks to teams. Adaptable planning should account for potential delays due to unforeseen circumstances like bad weather or supply shortages.
Measuring Success in Structural Steel Projects
Defining success in a structural steel project goes beyond meeting deadlines and budgets. It encompasses satisfying client expectations, achieving safety standards, and contributing to environmental sustainability. Conducting post-project evaluations can provide insights into what worked and areas for improvement in future projects.