Understanding Construction Safety Training
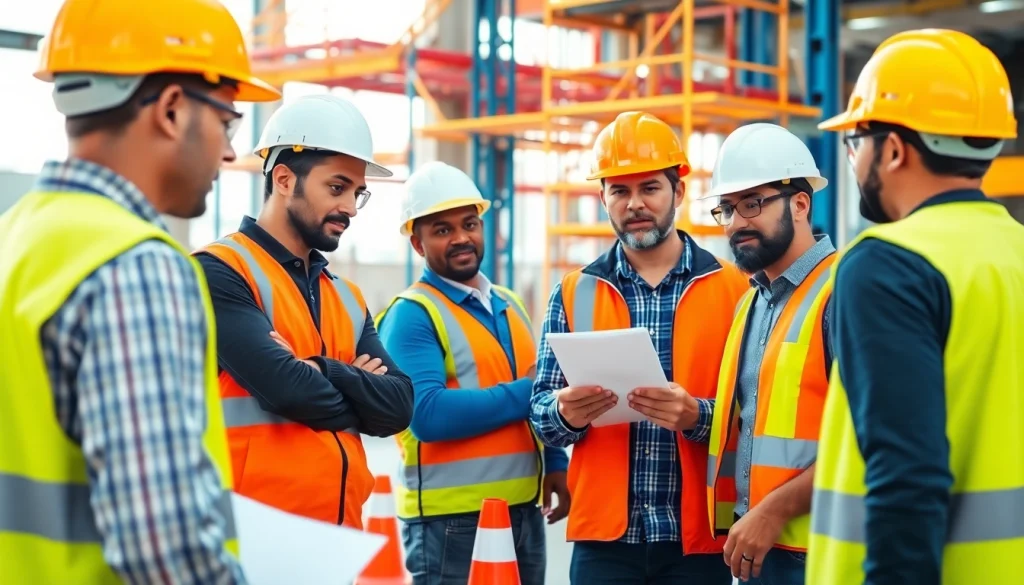
In today’s fast-paced construction industry, ensuring safety on the job site is not merely a regulatory requirement but a crucial aspect of operational success. Effective construction safety training is paramount to protect workers’ lives, enhance job efficiency, and promote a culture of safety within organizations. This training focuses on imparting the necessary knowledge and skills that workers need to recognize, prevent, and respond to hazards they might face on the job. With the complexities of construction projects increasing, so does the need for specialized and comprehensive safety training programs that align with industry standards and regulations.
The Importance of Safety Training
Safety training is critical in the construction sector due to the inherently dangerous nature of the work involved. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), one in ten construction workers are injured every year, making this workforce one of the most prone to accidents.
Having robust safety training can significantly reduce these statistics. Benefits of effective safety training include:
- Lower injury rates: Proper training equips employees with the knowledge to avoid hazardous situations, resulting in fewer accidents.
- Compliance with regulations: Adhering to safety protocols ensures compliance with OSHA and local regulations, helping companies avoid legal penalties.
- Enhanced worker satisfaction: Employees who feel safe and valued tend to be more productive and engaged.
- Improved company reputation: A strong safety record can enhance the credibility of a construction firm, attracting more clients and projects.
Key Components of Effective Training
For construction safety training to achieve its intended outcomes, several key components must be included in any effective training program:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and assessing potential hazards on site forms the foundation of any safety training program. This step enables trainers to design targeted scenarios that workers are likely to encounter.
- Hands-On Training: Engaging workers with practical exercises is essential. This could range from using equipment safely to practicing emergency response.
- Regular Updates: Regulations and methods evolve; hence, training should not be a one-time event but an ongoing process to incorporate the latest best practices and compliance updates.
- Training Documentation: Documenting training sessions, attendance, and assessments not only helps track progress but also serves as proof of compliance during audits.
Common Types of Construction Safety Training
Various training programs can be tailored to specific roles within the construction site. Some of the most common types include:
- General Safety Orientation: Provides a broad overview suitable for all employees regardless of their specific job roles.
- Fall Protection Training: Tailored for roles involving work at heights, this training instructs workers on practices and equipment that mitigate fall risks.
- Hazard Communication Training: Focuses on understanding hazardous materials and chemicals that workers may encounter.
- Machine Safety Training: Offers essential skills for operating heavy machinery, emphasizing safety protocols and maintenance practices.
- Emergency Response Training: Equips workers with skills and knowledge to respond effectively to emergencies, such as fires, medical issues, or natural disasters.
Components of a Successful Training Program
Developing a Training Curriculum
Crafting a successful training curriculum involves a systematic approach that assesses both organizational needs and legal compliance. Here is a step-by-step guide to developing a training curriculum:
- Needs Analysis: Identify specific safety issues at your construction site through risk assessment and employee feedback.
- Learning Objectives: Define clear, measurable goals for what the training will accomplish. For instance, workers should understand how to use fall protection equipment by the end of the course.
- Content Development: Create content that is engaging and relevant. Use a mix of instructional methods, including videos, presentations, and interactive elements.
- Facilitator Selection: Choose experienced facilitators who not only understand the material but also can convey it effectively to adult learners.
- Implementation: Launch the training program. Ensure all individuals participate by scheduling sessions at convenient times.
- Feedback Mechanism: Incorporate a method for attendees to provide feedback on the training, allowing for gradual improvements in future iterations.
Utilizing Hands-On Learning Techniques
Hands-on training techniques ensure that workers can apply what they learn in relatable, practical scenarios. Following are examples of effective hands-on training methods:
- Simulations: Use real-life situations to expose employees to hazards they may face on the job.
- Role-Playing: Allow workers to assume roles in emergency scenarios to enhance their problem-solving skills.
- Mentorship Programs: Pairing less experienced workers with seasoned mentors provides a platform for informal, on-the-job learning.
Assessment of Training Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of safety training is vital to ensure continuous improvement. Here are several key assessment strategies:
- Pre- and Post-Training Assessments: Administer quizzes before and after the training to quantify knowledge gains.
- Behavioral Observations: Regularly observe employee behavior on-site to assess the practical application of safety practices.
- Incident Rate Tracking: Monitor and analyze safety incident reports to evaluate whether training correlates with fewer accidents.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
OSHA’s Role in Construction Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets and enforces protective workplace safety and health standards. OSHA’s guidelines for construction sites are extensive and cover numerous aspects of workplace safety. Companies must be familiar with OSHA regulations to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of their workers. This includes:
- Ensuring all employees receive safety training before beginning work.
- Maintaining and providing access to safety data sheets for all hazardous materials.
- Conducting regular site inspections to identify and mitigate risks before they result in injuries.
Understanding Local Regulations
In addition to OSHA, local and state regulations often impose additional requirements. Understanding and complying with both federal and local regulations is paramount. Companies should continually assess local laws, as they may include specific training mandates, stricter safety protocols, or unique reporting requirements. Regular interaction with local industry bodies can provide construction companies with updates on key regulatory changes.
Implementing Best Practices for Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards requires diligence. Adopting best practices can result in seamless integration of safety into company culture:
- Continuous Education: Regularly conduct refresher courses to keep all personnel updated on changing laws and regulations.
- Documentation and Reporting: Document all training sessions and safety audits to provide evidence of compliance during inspections.
- Safety Committee: Establish a dedicated safety committee to oversee compliance efforts and encourage employee involvement in safety discussions.
Challenges in Construction Safety Training
Addressing Seasonal Workforce Fluctuations
The construction industry often experiences seasonal fluctuations in its workforce, posing a challenge to maintaining consistency in safety training. Temporary or seasonal workers might not have the same level of training as permanent employees. To address this challenge:
- Onboarding Programs: Implement comprehensive onboarding safety programs for seasonal workers to ensure they receive necessary training.
- Flexible Scheduling: Offer training sessions that consider the varied availability of a transient workforce.
Overcoming Language Barriers in Training
In a multicultural workforce, language barriers can impede effective safety training. Here’s how to tackle this issue:
- Multilingual Resources: Offer training materials in multiple languages relevant to the workforce.
- Visual Aids: Use diagrams, videos, and demonstrations to convey critical information irrespective of language proficiency.
- Peer Trainers: Employ bilingual trainers who can communicate in the primary languages of the workers.
Maintaining Engagement and Interest
Keeping participants engaged during safety training is crucial for information retention. Techniques include:
- Interactive Discussions: Encourage participation through discussions and questions during the training sessions.
- Gamification: Incorporate games or quizzes to make learning fun and interactive.
- Real-World Scenarios: Use case studies and simulations based on actual incidents to highlight the importance of adhering to safety protocols.
Future Trends in Construction Safety Training
The Impact of Technology on Safety Training
As technology evolves, so does the approach to safety training. Online resources and smartphone apps are streamlining safety procedures, allowing workers to access training materials and assessments on-the-go. A growing trend is the use of learning management systems (LMS) that offer tracking and reporting features for compliance and engagement metrics.
Virtual Reality Training Experiences
One of the most groundbreaking developments in safety training is the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) technology. VR creates immersive training experiences where workers can simulate high-risk scenarios in a safe, controlled environment. This hands-on approach boosts retention and prepares employees for real-life situations they may face on the job site.
Emphasizing Mental Health and Wellbeing
Beyond physical safety, there is a growing recognition of mental health in the workplace. Future safety training programs are likely to incorporate mental health education and resources. This may include training in stress management, conflict resolution, and fostering a supportive work environment. Ensuring the overall wellbeing of workers not only enhances safety but also contributes to higher morale and productivity.